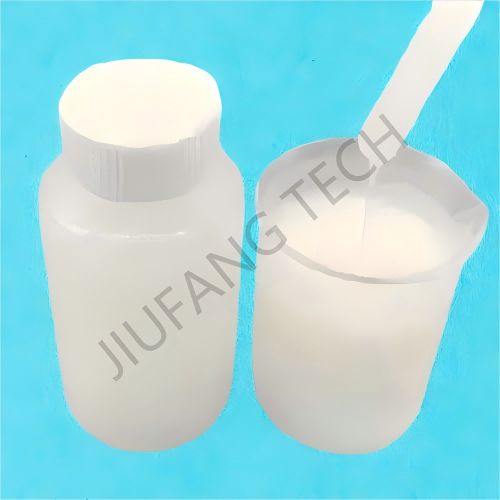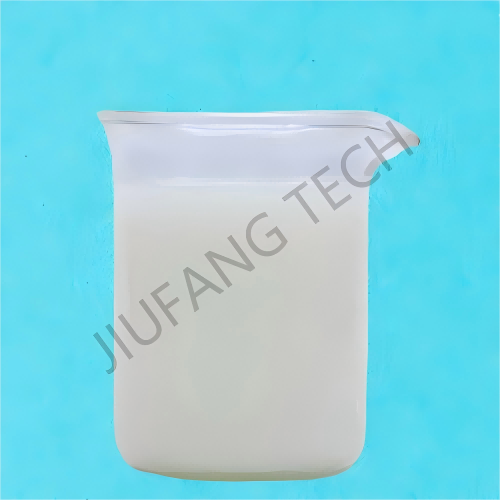
Emulsión CPAM para el tratamiento de aguas residuales
Marca JF
El origen de los productos Porcelana
El tiempo de entrega Plazo de entrega: 7 días
La capacidad de oferta 10000 TM/año
1. Cada mes nuestra fábrica puede producir 2000 toneladas de CPAM líquido y el producto CPAM líquido es un polímero reticulado.
2. Hemos cooperado con más de 300 clientes en CPAM para proyectos de tratamiento de agua.
3. Contamos con docenas de ingenieros destacados y podemos suministrar productos personalizados en el tratamiento de agua con emulsión CPAM.
descargar
Nombre
Líquido CPAM
Solicitud
CPAM para tratamiento de agua
CAS NO.
9003-05-8
Otros atributos
Apariencia
Emulsión blanca
Activar contenido
48%
Rango de viscosidad (ml/g)
1200~1600
Residuo
0,12%
Sustancia insoluble (%)
0.1
Carga catiónica
80%
Tiempo de disolución, min
Temperatura de almacenamiento,
°C
0~35
Vida útil, mes
Capacidad de suministro
Insufficient dosage: It cannot fully neutralize the charges of pollutants or bridge, resulting in small flocs, high turbidity, and high oil content in the effluent.
Excessive dosage: Excessive CPAM liquid molecules are adsorbed on the surface of particles, forming a "positive-charge encapsulation". Particles re-disperse due to the repulsion of the same charge (i.e., "re - stabilization"), and at the same time, it increases the cost of the agent and the COD of the effluent.
Optimal dosage: It needs to be determined through jar tests. Usually, for oilfield sewage, it is 5 - 50 mg/L (specifically adjusted according to the pollutant concentration and the performance of CPAM liquid).
2). Stirring Intensity and Time - The purpose of stirring is to evenly disperse CPAM liquid and make it fully contact with pollutants, but the intensity and time need to be controlled:
Mixing stage (1 - 5 minutes after dosing): Medium - to - high - intensity stirring (rotation speed 100 - 300 r/min) is required to ensure uniform dispersion of the agent and avoid excessive local concentration.
Flocculation stage (5 - 20 minutes after mixing): Low - intensity stirring (rotation speed 30 - 60 r/min) is required to promote the growth of flocs and avoid strong shear from breaking the formed flocs.
Insufficient stirring: The agent is unevenly dispersed, resulting in over flocculation in some areas and insufficient reaction in others.
Excessive stirring: The flocs are broken, and the sedimentation performance deteriorates.
3). Dosing Method - CPAM liquid needs to be prepared into an aqueous solution of a certain concentration (usually 0.1% - 0.5%) before dosing. Direct addition of solids should be avoided to prevent caking ("fish - eyes"), which affects dissolution and reaction. If step - by - step dosing (first adding a low - concentration solution and then replenishing after a certain interval) is adopted, the risk of "re - stabilization" can be reduced, and the flocculation efficiency can be improved.
4. Interference of Co - existing Substances
There may be other agents (such as demulsifiers, bactericides) or impurities in oilfield sewage, affecting the flocculation effect of CPAM liquid:
Synergistic effect: When used in combination with inorganic flocculants (such as PAC, FeCl₃), the inorganic agents first compress the double-electric layer, and then CPAM liquid plays a bridging role, which can improve the flocculation efficiency (for example, the "PAC + CCPAM" combination is commonly used in oilfield sewage).
Interference effect: If there are excessive anionic agents (such as anionic demulsifiers, sodium polyacrylate) in the sewage, they may react with the cationic groups of CPAM liquid to form precipitates, consuming the effective agent. In addition, reducing substances such as sulfides (S²⁻) and humic acid may destroy the cross - linked structure of CPAM liquid, reducing its stability.
The flocculation effect of cross - linked cationic polyacrylamide is the result of the combined action of the properties of the agent itself (cross - linking degree, cationic degree, molecular weight), the sewage water quality (pH, temperature, salinity, pollutant characteristics), operating conditions (dosage, stirring, dosing method), and co-existing substances.
In practical applications (such as oilfield sewage treatment), key parameters need to be optimized through small - scale and pilot - scale tests to balance the influence of various factors, so as to achieve efficient flocculation (such as oil content in the effluent < 10 mg/L, suspended solids < 20 mg/L).

Industry-specific attributes
| Name | CPAM liquid | |||
| Application | CPAM for water treatment | |||
| CAS NO. | 9003-05-8 | |||
Other Attributes
| Appearance | White Emulsion | |||
| Activate Content | 48% | |||
| Viscosity Range(ml/g) | 1200~1600 | |||
| Residue | 0.12% | |||
| Insoluble Substance(%) | 0.1 | |||
| Cationic Charge | 80% | |||
| Dissolving Time,min | 40 | |||
| Storage Temperature,℃ | 0~35 | |||
| Shelf Life,month | 12 | |||
Supply Ability
















